Today, two-thirds of Americans living with Alzheimer's dementia are women. What's the difference between dementia and Alzheimer's disease anyway? What are the causes? And what puts people at risk for dementia?
Use our visual guide to understand dementia, its most common causes, and symptoms.
What's the difference between dementia and Alzheimer's disease?
Dementia is a catch-all term for a group of symptoms including impairments in memory, language, and problem-solving. It has many causes, the most common of which is the brain changes associated with Alzheimer's disease.
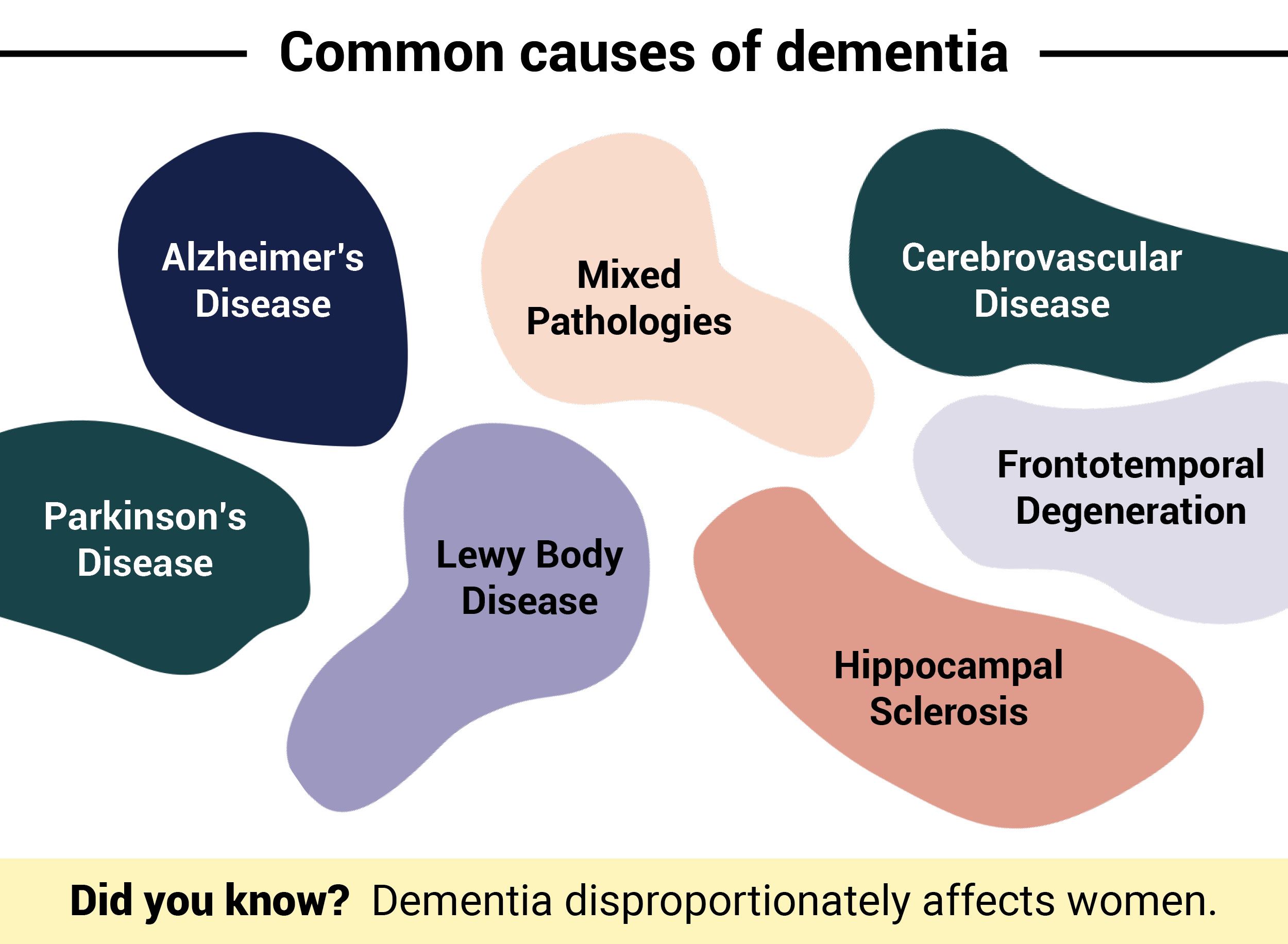
What are the most common causes of dementia?
The Alzheimer's Association's annual report outlines the most common causes of dementia and the symptoms that distinguish them. We've summed up those common causes here, but there are still a few other, rarer causes.
There are also times when a person may have symptoms that look like dementia but aren't. That sometimes happens as a result of the side effects of medication, untreated sleep disorders, thyroid problems, and even depression. Once those underlying medication or health issues are address, the symptoms usually resolve.
 Click infographic to enlarge.
Click infographic to enlarge.What are the risk factors for dementia?
Numerous factors also influence a person's risk of developing dementia, including age, genetics, and family history. Those risk three factors aren't changeable, but others are. These "modifiable risk factors" for dementia include cardiovascular health, smoking, physical fitness, diet, education, social and cognitive engagement, and traumatic brain injury.
Modifiable Risk Factors for Dementia
- Education
- Hypertension (cardiovascular health)
- Obesity
- Hearing loss
- Traumatic brain injury
- Alcohol misuse
- Smoking
- Depression
- Physical inactivity
- Social isolation
- Diabetes
- Air pollution
How does dementia affect women?
The majority of people living with dementia are women. Part of that is age, since women tend to live longer than men. But that's not the whole story. Evidence is mounting that gender inequality — and the sprectrum of ways it impacts women's lives — is also at play. Understanding the risk factors for women is critical to preventing and treating dementia in women and ensuring they age well.